Product Description
Our B Tyep Classical wrapped v belt have competite price and CZPT quality
Main conveyor belt products:
1) Wrapped V-belt (K, M, A, B, C, D, E; 3L, 4L, 5L, SA, SB, SC)
2) Narrow V-belt (SPZ, SPA, SPB, SPC; 3V, 5V, 8V)
3) Cutting edge V-belt (AX, BX, CX)
4) Cutting edge narrow V-belt (XPZ, XPA, XPB, XPC)
5) Timing belt
6) Duplex V-belt
7) V-belt for agricultural machinery-dimensions
8) V-belt for clothes washing machine
9) Automotive V-belt
10) Other types available CZPT
V belt, v belt fan belt, CZPT v belt, link v belt, v belt for washing machine, CZPT v belts, adjustable v belt, micro v belts, double poly v belt, CZPT v belt, micro rib v belts, hexagonal v belt, kevlar v belts, v belt distributors, poly v belt pulleys, large v belt
If you don’t inform us in advance, then we will produce the belt as per Li length
Features:
1) With special frames, our v-belts are resistant to heat, oil, fatigue, aging and friction.
2) Features: Large power, high speeds, long usage lives, small distortion, small sizes…
3) Applications: Electric motors, internal combustion engines, power transmission equipment.
4) We can provide these products in various sizes, and welcome buyer’s specifications.
Now we introduce belt as follows:
V-belt specialty with a core structure, rope core structure of the two, respectively, by wrapping cloth, top rubber, tensile body and the end of plastic is composed of 4 parts. The the rope core structure of the V-belt manufacturing convenient, general tensile strength, low prices, good toughness widely used special with a core structure of the V-belt, high strength, suitable for high speed occasions.
V-belt classification
The ordinary with core V-belt
Most of the V-belt with the core of the ordinary with core wire rope core, a small part of the carcass band core. Both with core structure are the fiber twisting or preparation, clip each fiber in the V-belt operation with core gradually elongation at break. Therefore, the use of ordinary V-belt line rope core and ply with core production can only be used in low-load transmission.
The special with core V-belt
The special with core V-belt with core polymer polyester steel brown silk the overall solid core rod with a core structure. As a whole due polyester steel brown silk solid core the untwisted structure, good adhesion, flex resistance, high strength, and do not run long, not only greatly improve the life of the rubber belts, but also the life of the belt body balanced, enterprises can maintenance-free, periodic replacement. On November 22 2571, the steel brown silk polyester skeleton material through the identification of the Committee of Experts: Brown silk with polyester steel structural skeleton as a transmission belt skeleton material with traditional polyester cord, hard rope, aramid fiber rope material belt life increased by 5-10 times compared to an international advanced level. Special with core belt ordinary belt high load heavy horsepower drive system frequently replaced much of the the world heavy industry companies favor.
V-belt applications FEATURES
Advantage
1, simple structure, manufacture, install less precision, easy maintenance, V-belt for larger occasions in the 2 axes of the central office
2, smooth transmission, low noise, cushioning shock absorbing effect
3, overload occurs, the drive belt from slipping on the pulleys can be prevented damage to the weak parts, from a security role
.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | NN500 |
|---|---|
| Material: | PU |
| Inside Material: | Fabric |
| Feature: | Oil-Resistant |
| Tensile Strength: | Strong |
| Transport Package: | Standard Sea Worthy Package |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are there any alternatives to V-belts for power transmission applications?
Yes, there are several alternatives to V-belts for power transmission applications. These alternatives offer different advantages and may be suitable for specific requirements. Here are some commonly used alternatives:
- Synchronous Belts:
- Flat Belts:
- V-Ribbed Belts:
- Chain Drives:
- Gear Drives:
- Direct Coupling:
Synchronous belts, also known as timing belts, are toothed belts that provide precise and synchronous power transmission. They have teeth on the inner side that mesh with corresponding grooves on the pulleys, eliminating slippage and ensuring accurate power transfer. Synchronous belts are commonly used in applications that require precise positioning, high torque transmission, or low maintenance.
Flat belts are thin, flexible belts that transmit power by friction between the belt and the pulleys. They offer a simple and cost-effective solution for power transmission. Flat belts are available in various materials, such as rubber, leather, or fabric-reinforced synthetic materials. They are suitable for applications with moderate power requirements and can be used in both light-duty and heavy-duty applications.
V-ribbed belts, also known as multi-rib belts or serpentine belts, are similar to V-belts but have a different cross-sectional shape. They have a flat or shallow V-shaped profile with ribs on the inner side, which engage with corresponding grooves on the pulleys. V-ribbed belts offer higher power transmission capacity and reduced slip compared to standard V-belts. They are commonly used in automotive applications, such as engine accessory drives.
Chain drives use a series of interconnected links to transmit power. They are known for their high strength, durability, and ability to handle heavy loads. Chain drives are commonly used in applications that require high torque transmission, such as industrial machinery, motorcycles, or bicycles. However, chain drives require periodic lubrication and maintenance to ensure proper operation.
Gear drives utilize interlocking gears to transmit power. They offer high efficiency, precise power transmission, and the ability to transmit large amounts of torque. Gear drives are commonly used in applications that require high precision, such as robotics, machine tools, or automotive transmissions. However, they can be more complex and expensive compared to belt drives.
In some cases, power transmission applications may utilize direct coupling, where the motor shaft is directly connected to the driven equipment without the use of belts or other intermediate components. Direct coupling offers high efficiency, compactness, and eliminates the need for belt maintenance. It is commonly used in applications with high torque requirements or where precise alignment is critical.
The choice of the alternative to V-belts depends on various factors, including the specific power transmission requirements, space limitations, cost considerations, maintenance needs, and the desired level of precision. It is important to evaluate these factors and consult with experts to select the most suitable alternative for a particular application.
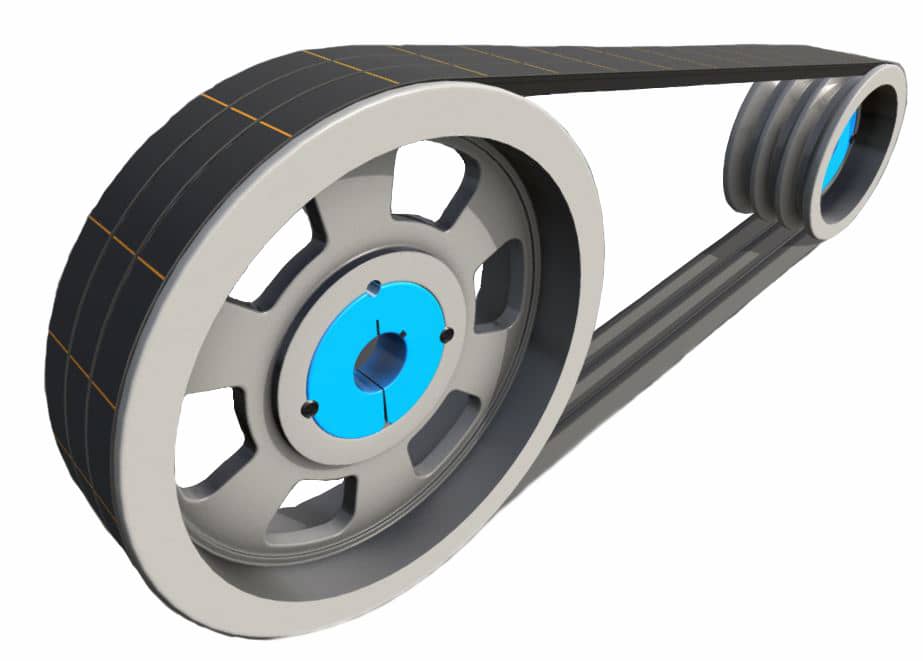
How do you troubleshoot common issues with V-belts, such as slipping or squealing?
Troubleshooting common issues with V-belts, such as slipping or squealing, is essential to maintain the proper operation and efficiency of the belt drive system. Here are some troubleshooting steps to address these issues:
- Slipping:
- Check the belt tension: Insufficient tension is a common cause of slipping. Ensure that the V-belt is properly tensioned according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Adjust the tension by using the appropriate tensioning method or tools.
- Inspect for wear or damage: Examine the V-belt for signs of wear, cracks, fraying, or other damage. A worn-out belt may not provide adequate grip and can lead to slipping. Replace the belt if necessary.
- Check pulley alignment: Misaligned pulleys can cause the belt to slip. Verify that the pulleys are properly aligned both parallel and angularly. Adjust the pulley positions if misalignment is detected.
- Assess pulley condition: Worn or damaged pulleys can contribute to belt slipping. Inspect the pulleys for wear, rough surfaces, or damage. If needed, replace the pulleys to ensure proper belt engagement.
- Verify the load and application: Excessive loads or improper application can cause the belt to slip. Ensure that the belt drive system is designed and rated for the specific load requirements.
- Squealing:
- Check belt tension: Insufficient or excessive belt tension can lead to squealing. Adjust the tension to the recommended range specified by the manufacturer.
- Inspect for wear or contamination: Check the V-belt for signs of wear, glazing, or contamination. Worn or contaminated belts may produce squealing noises. Replace the belt if necessary and eliminate any contamination from the belt or pulleys.
- Examine pulley condition: Damaged or worn pulleys can create noise. Inspect the pulleys for wear, damage, or rough surfaces. Replace any worn or damaged pulleys.
- Verify pulley alignment: Misaligned pulleys can cause the belt to run at an angle, resulting in noise. Ensure that the pulleys are correctly aligned both parallel and angularly. Adjust the pulley positions if misalignment is detected.
- Check for belt glazing: Belt glazing occurs when the belt’s contact surface becomes smooth and glossy, reducing traction. If glazing is present, roughen the belt’s surface with fine sandpaper or replace the belt if necessary.
- Assess environmental factors: Environmental conditions, such as excessive heat or humidity, can affect belt performance. Ensure that the belt drive system operates within the recommended temperature and humidity ranges.
Slipping occurs when the V-belt fails to maintain proper traction with the pulleys, resulting in reduced power transmission and potential belt wear. To troubleshoot slipping issues:
Squealing noises from V-belts are often caused by vibrations, misalignment, or improper tension. To troubleshoot squealing issues:
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can identify and address common issues with V-belts, such as slipping or squealing. Regular maintenance, proper tensioning, and alignment are crucial for ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of the belt drive system.

How do you properly install and tension a V-belt for optimal performance?
Proper installation and tensioning of a V-belt are crucial for achieving optimal performance and ensuring its longevity. Here are the steps to properly install and tension a V-belt:
- Select the appropriate V-belt: Determine the correct V-belt size and type based on the application requirements, including pulley diameters, power transmission needs, and environmental factors.
- Clean the pulleys: Ensure that the pulleys are clean and free from any contaminants, such as dirt, debris, or oil. Clean the pulley grooves using a brush or compressed air to ensure proper belt grip.
- Inspect the pulleys: Check the pulleys for any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Replace or repair any damaged or worn-out pulleys before proceeding with the installation.
- Place the V-belt on the pulleys: Position the V-belt on the pulleys, ensuring that it is properly seated in the pulley grooves. Make sure the belt is correctly aligned with the pulleys and is not twisted or kinked.
- Adjust the center distance: If necessary, adjust the center distance between the driving and driven pulleys to the recommended specifications provided by the manufacturer. This ensures proper belt tension and alignment.
- Tension the V-belt: The correct tension is crucial for optimal V-belt performance. Use a tension gauge to measure the belt’s tension. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines or recommended tension specifications for the specific V-belt type and application.
- Apply tension gradually: Apply tension to the V-belt gradually and evenly. Avoid sudden or excessive tensioning, as it can lead to belt damage or pulley misalignment. Follow the recommended tensioning procedure provided by the manufacturer.
- Check the belt tension: After tensioning the belt, recheck the tension using a tension gauge. Ensure that the tension falls within the recommended range for the specific V-belt type and application. Adjust the tension if necessary.
- Verify alignment: Confirm that the pulleys are aligned properly. Check for any misalignment or belt tracking issues. Make adjustments as required to ensure the belt runs smoothly and centrally on the pulleys.
- Perform a test run: After installation and tensioning, perform a test run of the V-belt system. Monitor the belt’s performance, including proper grip, minimal vibration, and absence of noise. Address any issues or abnormalities promptly.
It is important to refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and specifications for the specific V-belt type and application. They may provide additional instructions or considerations for installation and tensioning.
By following these steps and adhering to the manufacturer’s recommendations, you can ensure the proper installation and tensioning of a V-belt, leading to optimal performance, reduced wear, and extended belt life.


editor by CX 2024-04-25
by
Leave a Reply